
Noisy snapshots show quantum
weirdness
Researchers from the University of Colorado
have devised a relatively simple way to detect a pair of entangled, or
linked atoms.
The properties of entangled atoms, including magnetic orientation,
or spin, remain linked regardless of the distance between the atoms.
The detection ability advances quantum computer and quantum communications
research. Quantum computers and communications equipment use properties
of particles like atoms to store, manipulate and transport information.
Entangled particles are well-suited to carry out the basic logic operations
of quantum computers and to teleport particles. Quantum computers could,
in theory, solve certain large problems orders of magnitude faster than
classical computers.
Key to the researchers' method is it does not involve the difficult
task of detecting single atoms. Instead, the method measures noise --
fluctuations in images of clouds of atoms. The method also gives researchers
a useful tool for studying all kinds of atomic phenomena including ultracold
gas clouds, where it is difficult to identify individual atoms.
To measure the image fluctuations the researchers cooled atoms
confined to an optical trap, used a magnetic field to coax pairs of atoms
to form molecules, then used a different magnetic field to break up the
molecules, leaving the pairs entangled and flying apart in opposite directions.
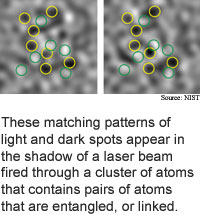
They then fired a laser at the atom cloud and recorded the light
scattering off the atoms with a digital camera. Identical patterns in
the digital images revealed the entangled pairs.
Researchers generally agree that practical quantum computers are
one to two decades away. The work appeared in the March 25, 2005 issue
of Physical Review Letters (Probing Pair-Correlated Fermionic Atoms
to Correlations and Atom Shot Noise).
Stories:
Memory mimic aids reading
Chip gauges cell reactions
View from the High Ground:
NYU's Nadrian Seeman
Briefs:
Surface tension drives nanomotor
Laser sniffs explosives
Nano pyramids boost fuel cells
Noisy snapshots show quantum weirdness
Research Watch blog
View from the High Ground Q&A
How It Works
RSS Feeds:
News
Ad links:
Buy an ad link
Ad links: Clear History
Buy an ad link
|
TRN
Newswire and Headline Feeds for Web sites
|
© Copyright Technology Research News, LLC 2000-2010. All rights reserved.